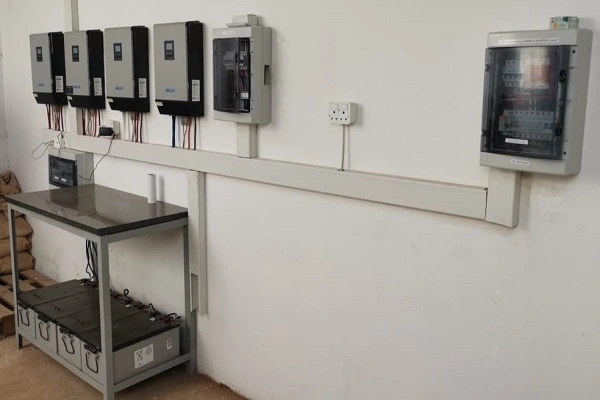
3-Phase power
The different applications and uses.
Residential 3-phase Power
Residential
Three Phase power is generally reserved for more industrial applications, although a house may have 3 phases fed to the DB (Distribution Board) it is seldom the case that 3-phase power is actually used.
3-phase power is made up of three single phases that cycle 120 degrees apart from one another, thus forming a balanced energy supply.
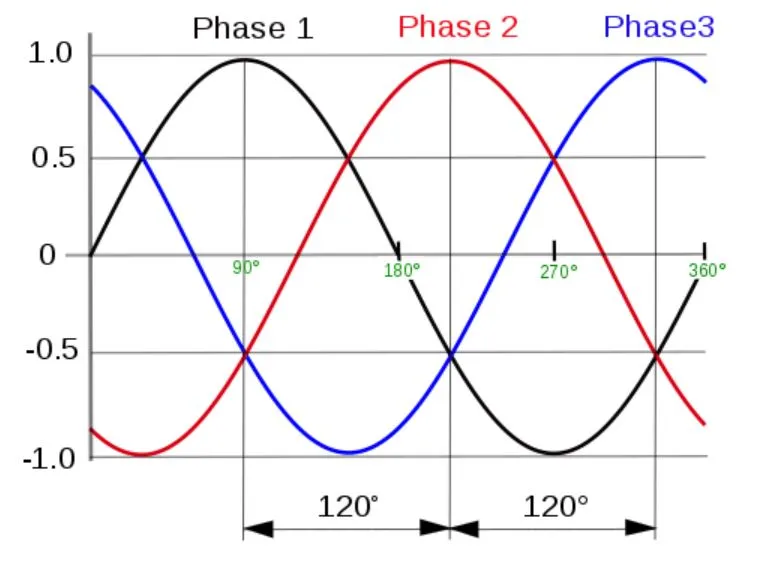
Let us clarify the differences between them.
In South Africa, we do not make use of only two phases.
An electrical appliance will either use 3-phases of power or a single one of the three phases.
Single phase power is more commonly used in homes than one might believe.
Houses with 3-phase power generally split the three phases into three single phase circuits, one to power lighting and plugs, another to power geysers and the last to power under-floor heating or other large loads such as walk-in fridges.
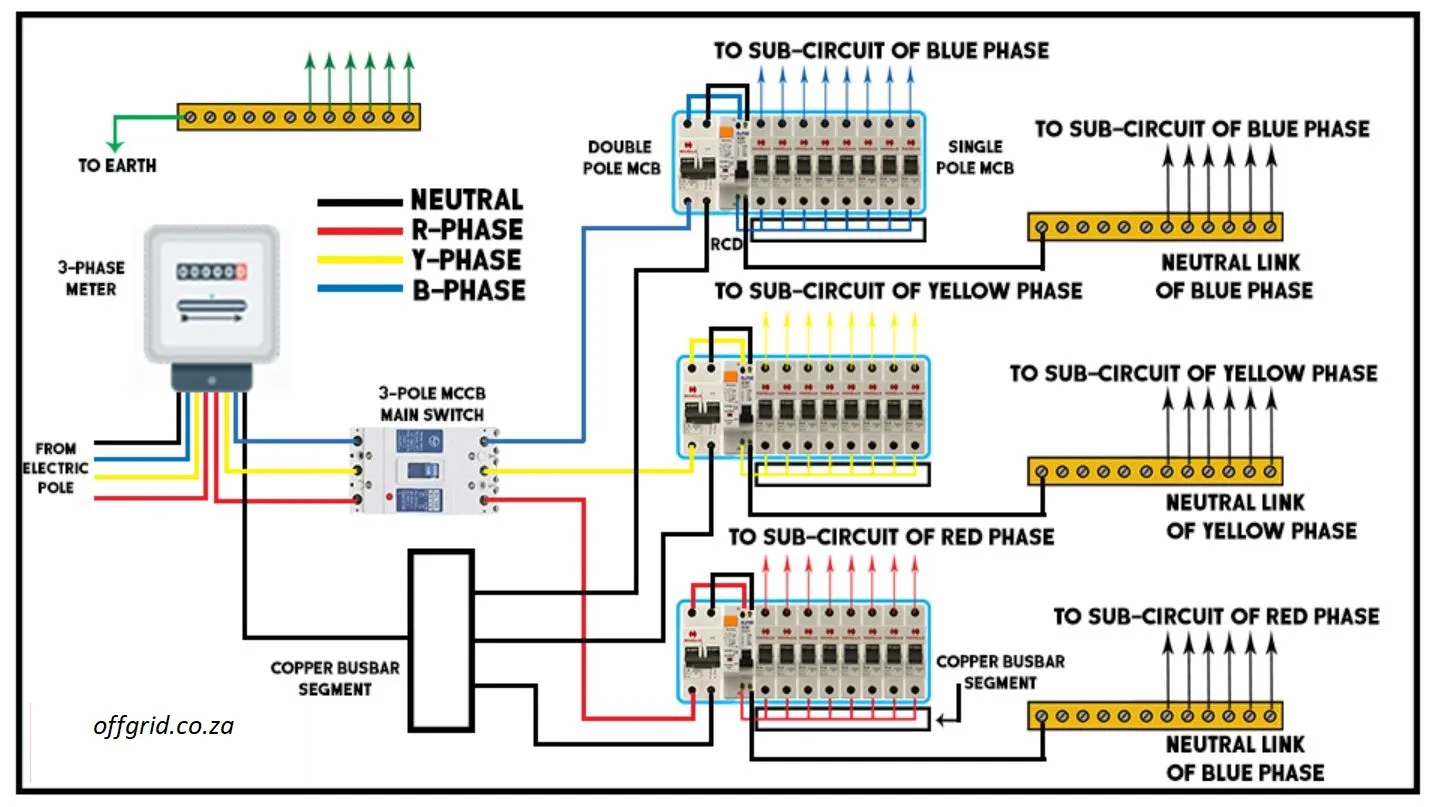
Single VS Three-Phase
A Single-phase can supply a massive amount of power, where a single phase starts to struggle is when it is used on inductive loads such as electrical motors.
Electrical motors that use single-phase power start to become very inefficient at around 2200w-2500w this is when 3-phase power comes in handy, it can supply far more powerful motors than that as the time between sine-wave peaks is a lot less.
As 3-phase power is mostly intended for heavier machinery, the inverters used to supply 3-phase power are generally true sine wave units.
Commercial 3-Phase Power
The use of 3-phase power to drive large inductive motors and machinery is nothing new in the farming and industrial sectors, offering its own set of technical challenges and benefits.
Everyone who has worked with 3-phase machinery knows all too well what implications come from a lost phase.
Pure sine wave 3-phase inverters protect these machines from phase failure as well as power surges. However, no factory or work-shop run solely on 3-phase power, Single-phase power is also used to power smaller machines and office equipment.
Balancing loads on 3-phase inverters can prove quite a tricky task as well. This is easily solved by using piggy back inverters. These inverters are single-phase units which can be connected to operate in a single or three-phase configuration, or BOTH. This is a very handy way of balancing 3-phase as well as single-phase loads.
When considering an inverter setup to run industrial machinery, transient currents will need to be measured in order to gauge the size of inverters to be used.


